FPGA VME Bridge Replacement for End of Life Tsi148
X-ES Has Your Solution to the End of Life (EOL) Tsi148 VME Bridge
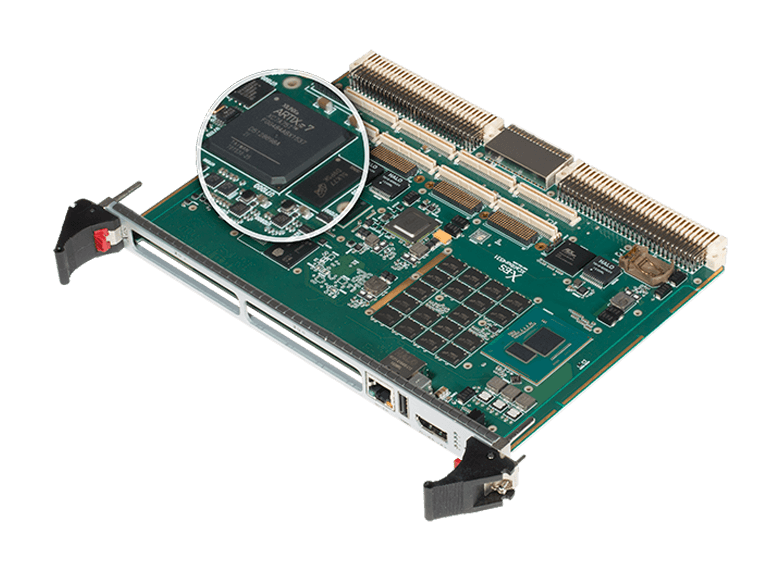
6U VME products with an integrated AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 FPGA VME Bridge designed to be pin-compatible with the Radstone/GE/Abaco PPC7D VME IDT Tsi148-based card, providing users with a straightforward, disruption-free upgrade path for legacy systems.
Future-Proofing VME Systems
X-ES selects an FPGA-based VME solution enabling high performance VMEBus capability on our flagship SBCs. Offering a wide variety of valuable features beyond what the Tsi148 VME Bridge had been capable of, the AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 VME Bridge supports a x4 PCI Express Gen2 to the host interface and supports an external DDR3 SDRAM DMA buffer.
With its firmware upgradeable design and support for future portability of IP to a new chip, X-ES VME boards offer system integrators a VME Bridge solution devoid of components subject to lifecycle concerns, in an even smaller chip package than had previously been available.
An Evolution & Extension Beyond the Tsi148
1981
VMEBus32 protocol introduced, with BLT transfer at 40 MB/s, connecting the processing subsystem with VMEBus.
1987-2003
VMEBus protocol continues to grow and develop, most recently supporting 2eSST transfer at 320 MB/s on a 5-row connector.
2015
Production of the IDT Tsi148 VME Bridge ceases, rendering the majority of the industry’s current VME products obsolete.
2016
X-ES chooses the AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 FPGA-based VME Bridge as the feature-rich technology to continue our VME products.
A History of VMEBus Technology
The VMEBus form factor has been a fundamental building block of high-end embedded computing systems for more than 30 years, stretching back to the introduction of the VMEBus32 protocol in 1981.
A desire to connect non-68000 series processing boards, such as PPC and x86 processing subsystems which do not natively support the 68000-style connector, required a bridge chip to connect PCI to the VMEBus.
PCI to VME Bridge chips were thus built to allow processing subsystems to access the VMEBus. Tundra (IDT) introduced the Universe II in 1997, which supported PCI-to-VME64. In 2004, Tundra/IDT began selling the Tsi148 VME Bridge, which supported PCI-X-to-VME64/VME320. The Tsi148 quickly became a standard component in many of the embedded computing industry’s VME boards.
A Look Into the Future of VME
In 2009, Tundra was acquired by IDT; the Tsi148 VME Bridge continued to be manufactured at IBM’s Essex Junction fabrication facility.
Five years later, IBM decided to exit the semiconductor chip manufacturing business, citing lack of financial feasibility. The fate of the industry’s main VME Bridge was sealed, with the Tsi148’s EOL announcement in 2014.
X-ES is committed to VME and the many systems that rely upon its proven technology. With our cutting-edge FPGA-based VME Bridge, X-ES is able to offer more features and functionality than had ever previously been available with a traditional VME Bridge. Our Intel® and NXP 6U VME SBCs come standard with high-performance processing capabilites, a wide variety of I/O support including Ethernet, USB, and serial, and are backed by our top-tier team of engineers.
X-ES VME SBCs & Carriers Featuring the
AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 VME Bridge
XCalibur1931
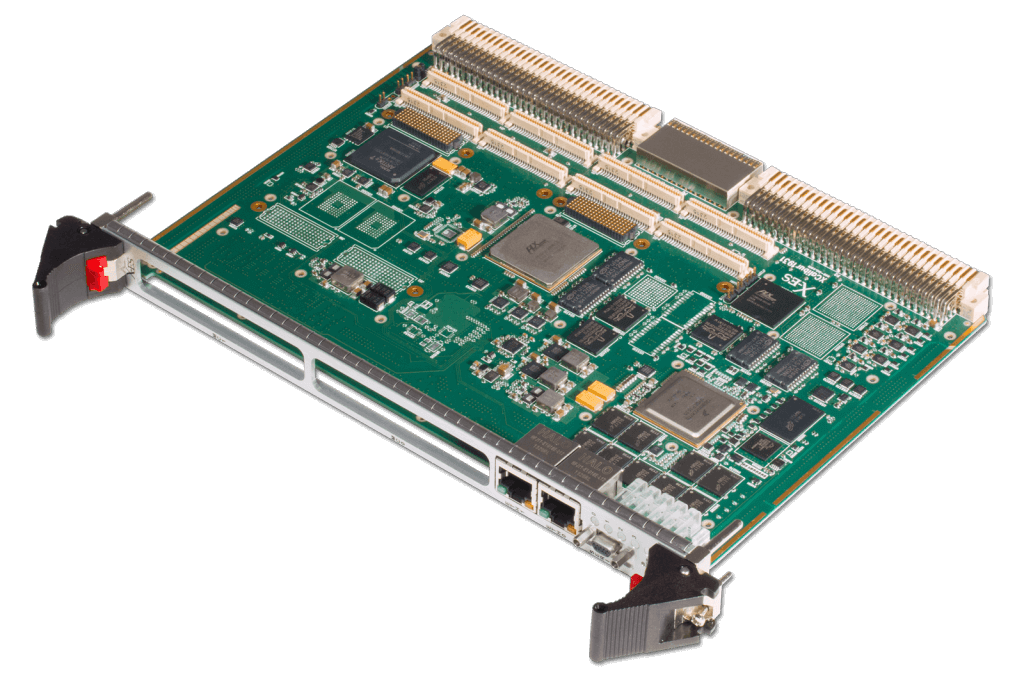
The XCalibur1931 is a high-performance, 6U VME SBC that was designed to be pin-compatible with the Radstone/GE/Abaco PPC7D VME card, providing users with a straightforward, disruption-free upgrade path for legacy systems. The NXP QorIQ T2080 processor coupled with up to 8 GB of DRAM, up to 32 GB NAND flash, and two XMC/PMC sites provides a significant performance boost over the PowerPC 7447.
The XCalibur1931 supports six Gigabit Ethernet ports, PMC I/O, and RS-232/422/485 serial ports out the P2 backplane connectors. The front panel supports two Gigabit Ethernet ports, RS-232 serial, and an optional USB 2.0 port.
View XCalibur1931XCalibur4531
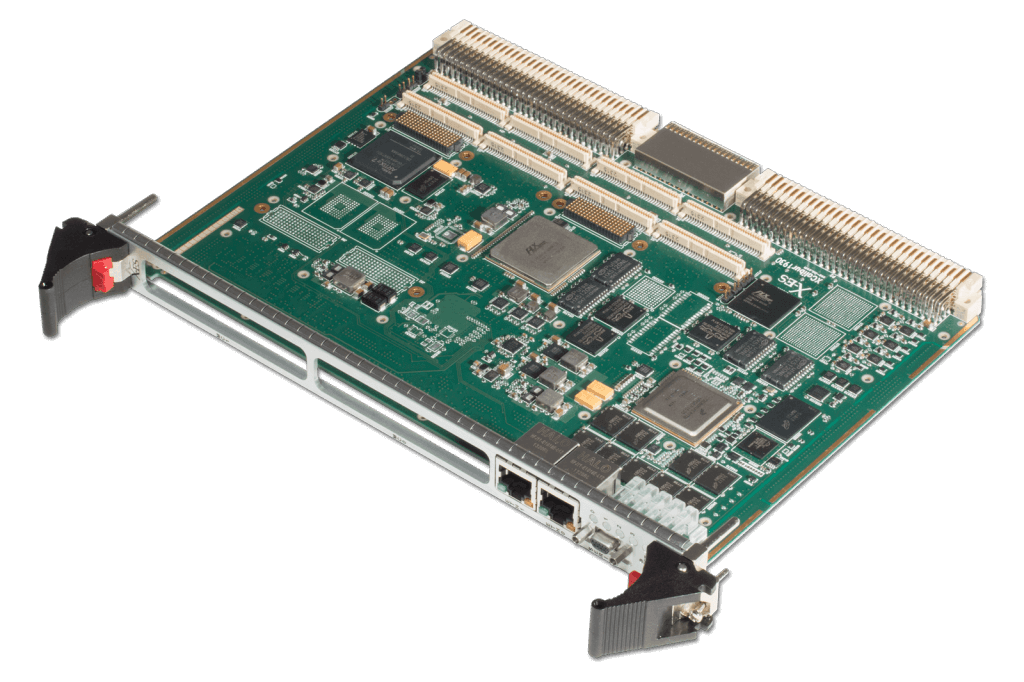
XCalibur4531 is a 5th Generation Intel® Core™ i7 6U VME SBC featuring an AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 FPGA-based VME bridging solution. By implementing an FPGA-based VME bridge, the XCalibur4531 mitigates obsolescence concerns prevalent in aging VME systems. XCalibur4531 supports VME32, VME64x, and 2eSST operation for easy integration into existing VME systems, making it the optimal choice to give your application a processing performance boost.
XCalibur4531 supports up to 16 GB ECC SDRAM, 64 GB onboard SSD storage, and hosts two XMC or PMC modules. XCalibur4531 is available in both air- and conduction-cooled assemblies with standard I/O interfaces including serial, video, USB, Ethernet, and SATA.
View XCalibur4531XCalibur1930
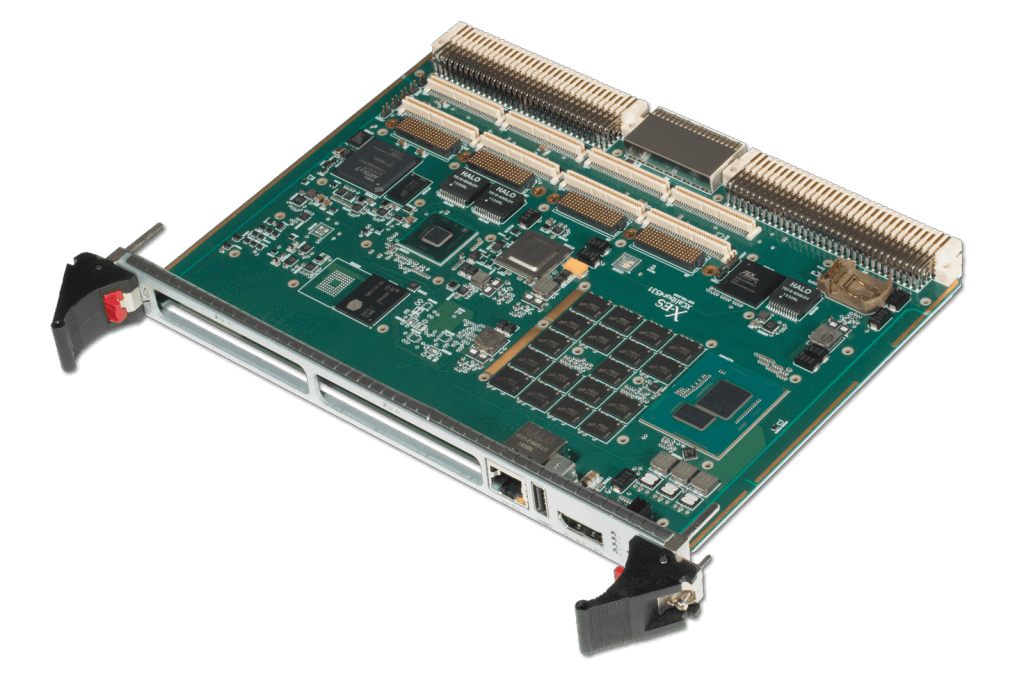
The XCalibur1930 is a high-performance, 6U VME, multiprocessing, single board computer featuring an NXP QorIQ T2080 processor with four dual-threaded e6500 cores running at up to 1.8 GHz, each with a 128-bit AltiVec SIMD unit.
The XCalibur1930 provides up to 8 GB of DDR3-1866 ECC SDRAM, two XMC/PrPMC slots, and 512 MB of NOR flash (with redundancy). It also supports Gigabit Ethernet, PMC I/O, USB, SATA, and RS-232/422/485 serial ports out the P2 backplane connectors. The front panel supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, USB, and RS-232 serial ports.
View XCalibur1930XChange4003
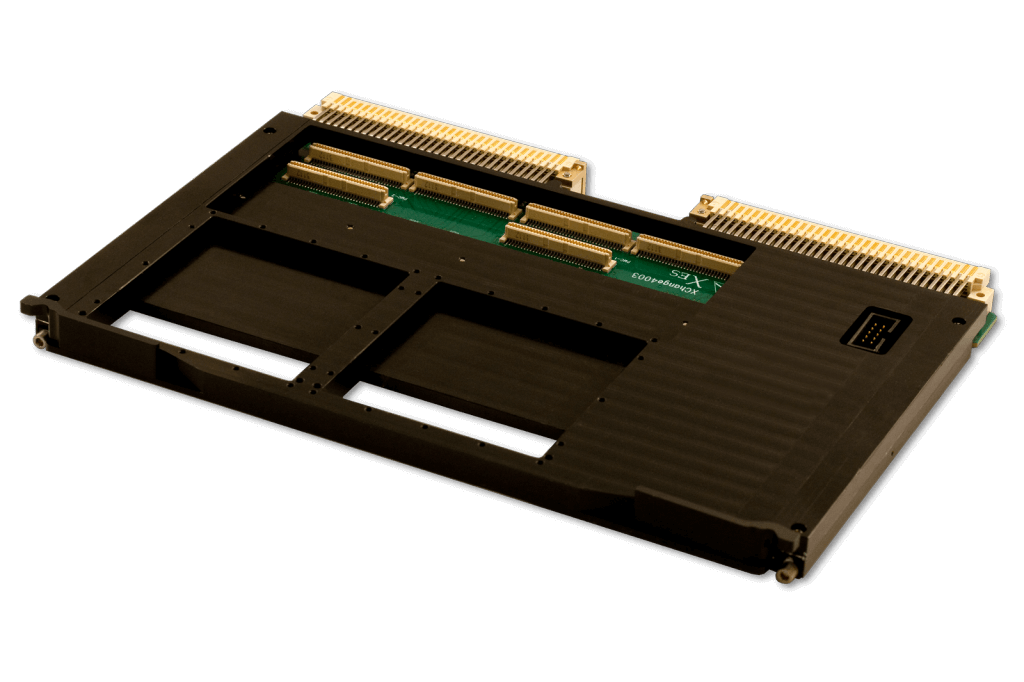
XChange4003 is a VME64x carrier card that facilitates connectivity of XMC/PMC modules to the VMEBus, by utilizing an AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 FPGA-based VME bridging solution. The FPGA-based VME bridge solution assures long production life and high performance operation.
XChange4003 supports all deployed versions of the VMEBus protocol, from the original VME32 up through VME64x and 2eVME/2eSST operation, making it an effective solution for interfacing any XMC/PMC module to any system’s VMEBus backplane.
XChange4003 supports both intelligent (Monarch PrPMC/Root Complex PrXMC) and non-intelligent (PMC/endpoint XMC) boards, and can operate in a SYSCON or non-SYSCON VMEBus slot.
View XChange4003Speak to Our VME Experts Today!
Let X-ES’ team of talented engineers handle your next VME project,
utilizing our innovative AMD (formerly Xilinx) Artix-7 FPGA-based VME bridge solution.